Physics Demo Number: 137
Approximate
Run Time: 10 min
Microwave Optics and Evanescent Wave Tunneling Through A Split Prism
Demo Description
A microwave generator and two receivers are used along with two paraffin prisms to show evanescent wave tunneling.
Scientific Principles
-
Microwave Optics and Evanescent Wave Tunneling
- Some sources may refer to 'frustrated total internal reflection' in this arrangement of elements.
Equipment
-
Microwave generator and receivers.
-
Paraffin Prisms.
Equipment Location
-
Kit (137) on [A-1-5]
Instructions
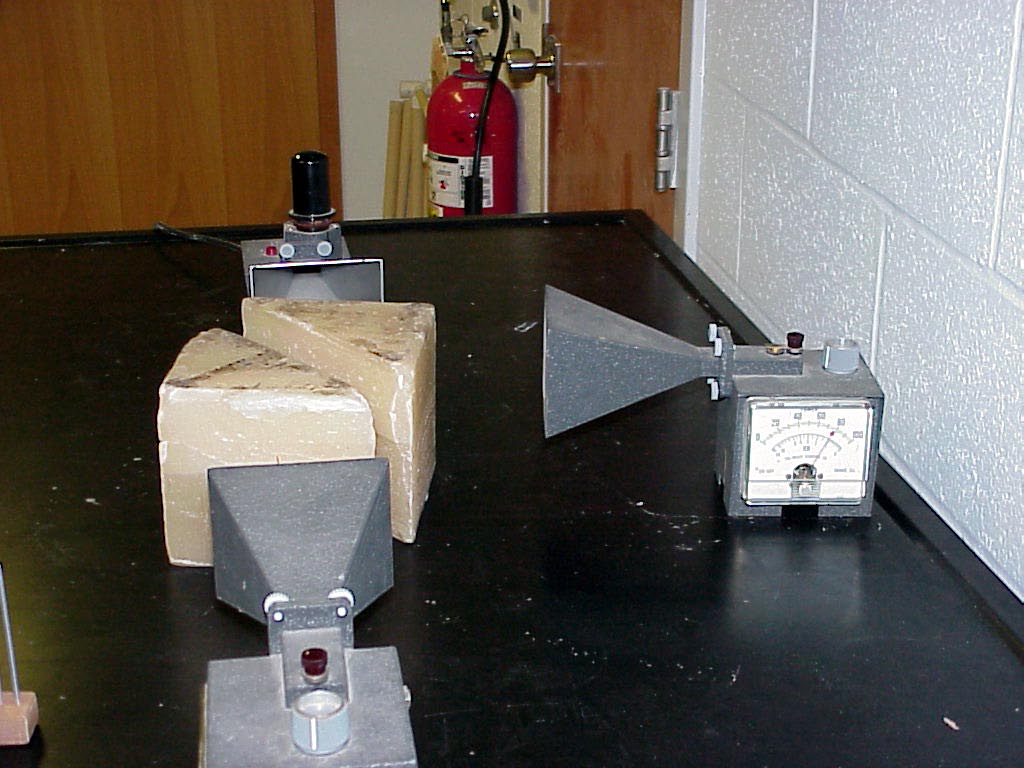

In
the back of the first photo is the microwave generator (gray unit
with black vacuum tube sticking out of its top).
It is sending microwaves towards the receiver in the foreground.
Notice that a good bit of the beam is being totally internally reflected to the receiver at the right by the paraffin right angle prism nearest the generator.
The second photo
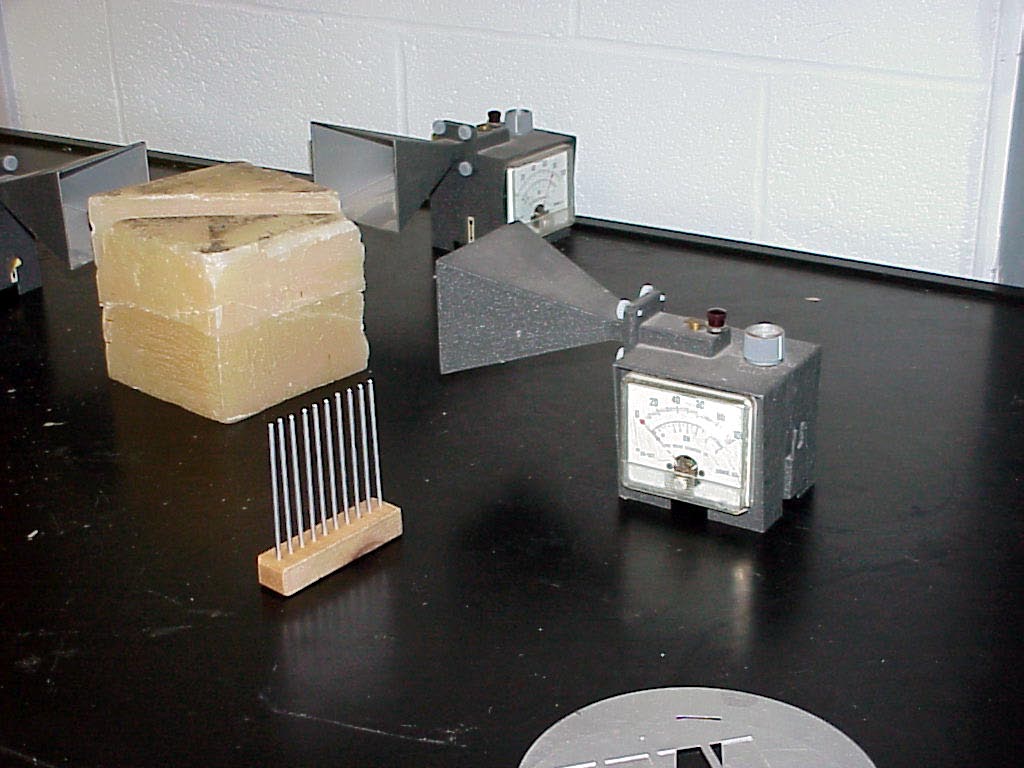
shows
a closer view of the state of affairs just described , with only
the camera having been moved around about 90 degrees to the left.
The next photo
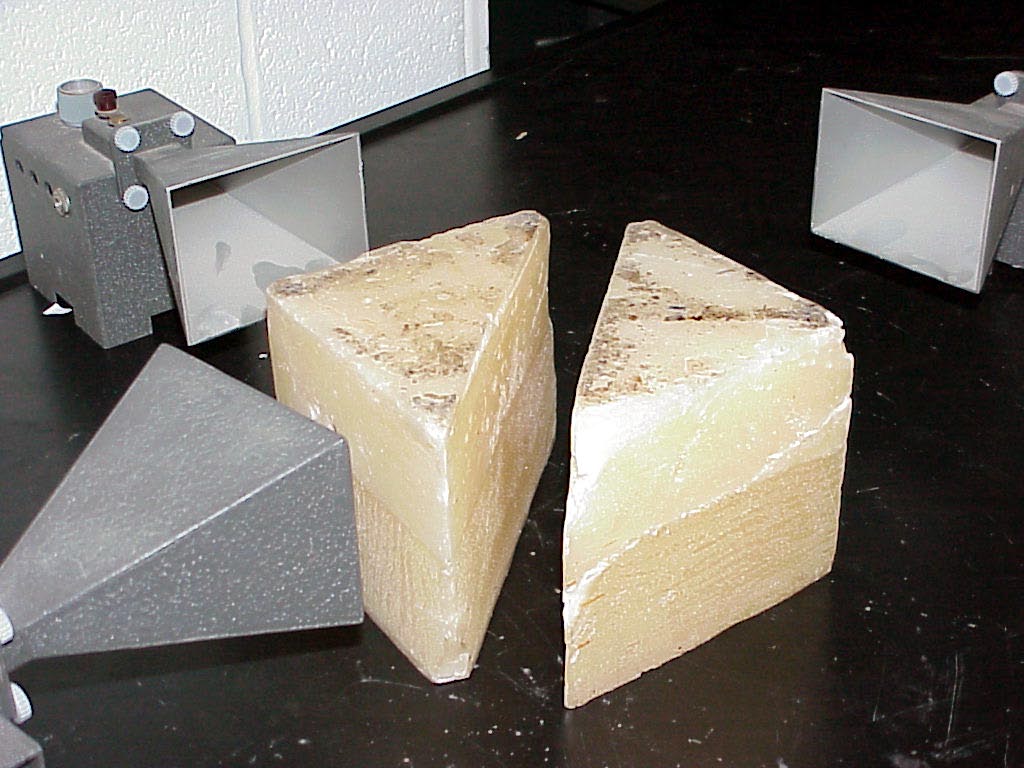

gives
the view obtained by moving the camera about 45 degrees more to
the left.
Notice that the second 90 degree prism is not very close to its twin prism.
The next photo
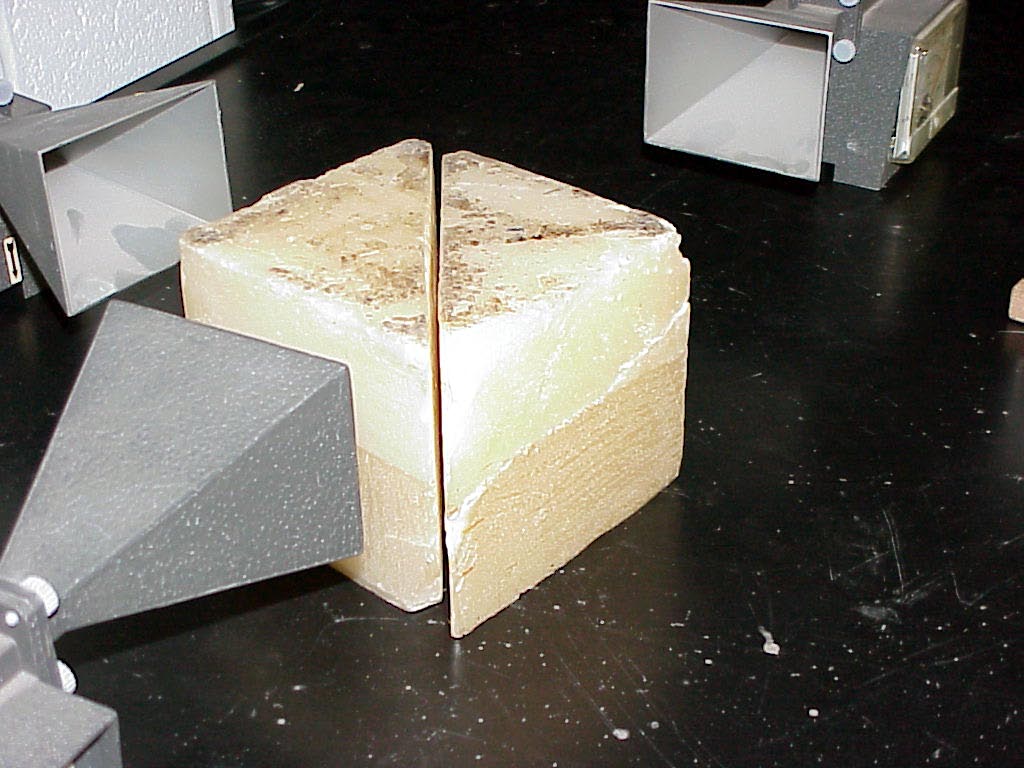

depicts
the five elements from the same camera angle as the previous
picture, but now the right prism has been carefully slid up quite
close to its mate, but without physical contact between their long
faces. However this change of the positioning of the right prism
has resulted in the new state of receiver readings shown in the
next photo,
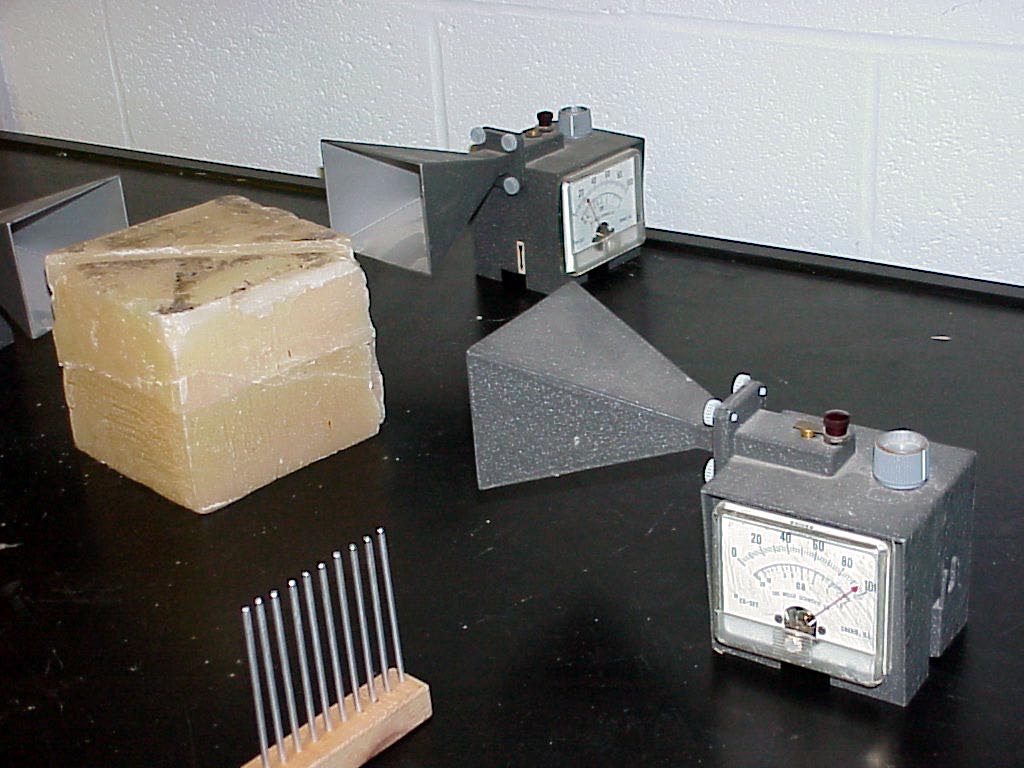
where
the camera has now been put back to its view as in the second
photo.
Notice that the very close physical proximity of the second prism face to that of the undisturbed first prism face has resulted in the reappearance of a large beam energy back to the the primary receiver . Moreover the energy traveling to the side receiver has abated sharply.
The five microwave elements live in Kit (137) on [A-1-5].
Writeup created by David A. Burba
Copyright © 2011, Vanderbilt University. All Rights Reserved.