Physics Demo Number: 042 |
Approximate Run Time: 10 min |
|||
Basic Electrostatics With Rods, Furs, Silk and Electroscopes |
||||
Demo DescriptionRub silk on a glass rod to create a positive charge on the rod. Rub fur on a plastic rod to charge the rod negatively. |
Scientific Principles
|
|||
|
Equipment
|
|
|||
|
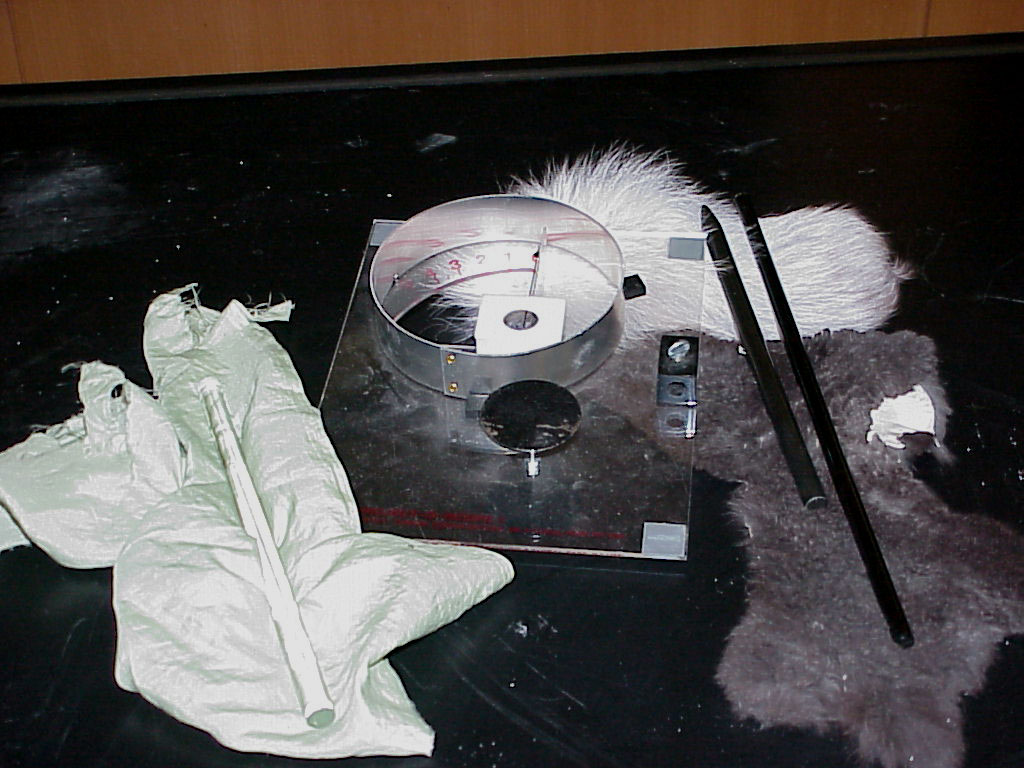
Equipment Location The pictured items reside in Kit (042) on [B-1-4]. |
||||
InstructionsThe greenish cloth on left is silk and can be used with the glass rod to make the rod positive. The furs on right can be used to leave a negative charge on the black plastic rod. (Alternate silk cloth includes brown burlap-looking and rough-feeling , but pure silk cloth.) The electroscope can be used on the overhead projector or document camera to display charges on rods. One simply lays a charged rod on the black disc and swipes the rod along its entire length against the disc, perhaps repeating the swiping process a few times for maximum deflection of needle. Alternatively one may leave the charged rod laying on the black disc, if the first method does not yield a satisfactory deflection of the needle. One may also lay a soda can on its side on the lecture table and set it into rolling motion by attraction from a negatively charged black rod. With all the electrostatics demos, there is an option for reducing the effects of excessive humidity. Simply warm the components with the dedicated heat gun. The gun normally resides on the repair bench I . The bench is on the wall next to the Science Library just before the [H] columns.
Please note, this is a Heat Gun, not a hairdryer! Use sparingly and carefully to avoid burning yourself , setting something on fire ,or ruining the demonstration components!! |
||||
Writeup created by David A. BurbaCopyright © 2013, Vanderbilt University. All Rights Reserved. |
||||