Acids and Bases
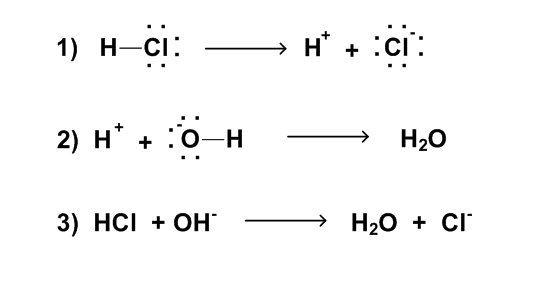
In this reaction, the breaking of an HCl bond forms a proton (electron pair acceptor). This proton then reacts with the base (electron pair donor) to form a new product. An acid-base reaction yields acids and bases as products. These new acid and bases are termed conjugates. Each acid reactant has a conjugate base product, and each base reactant has a conjugate acid product. These reactant and product pairs are termed conjugate acid-base pairs.
Different acids and bases have varying strengths. The strength of these species is dependent upon several factors such as solubility, bond strength, and ion stability. The strength of an acid is expressed in terms of pH. The pH scale ranges from 1 - 14 and is unitless. A solution with a pH of 7 is neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is basic. The stronger the acid the lower the pH value, and the weaker the acid the higher the pH value.
![]()